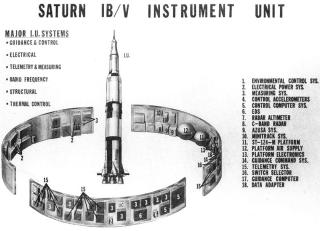
飛行制御機器(IU)
- 直径:260in (6.604m)
- 高さ:36in (0.9144m)
- 平均重量:4500lb (2.04ton)
- 製造:IBM (International Business Machines Federal Systems Div. Huntsville, Ala.)
構造
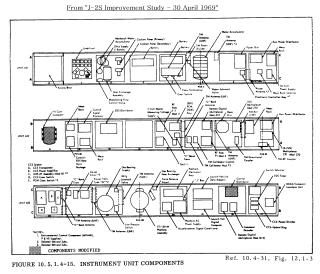
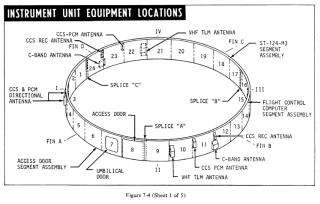
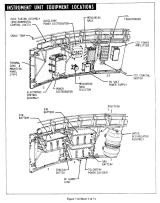
SaturnV の IU は、SaturnI で使用されたものをベースにして、NASA MSFC(マーシャル宇宙飛行センター)によって開発され、組み立て、製造、テストはIBMが請け負った。 IUには、誘導、追跡、位置決め、データ通信に必要な電子機器が組み込まれている。 本体は3つの内角120度のアルミニウムハニカムのパーツを円形に組み合わせ、上下にアルミニウム合金のチャネル材を取り付けることによって構成される。 地上設備とIU内部の機器をつなぐumbilical(へその緒)コネクタには、スプリングで閉じるカバーがもうけられている。 その隣には、ロケット組み立て後に作業員が中にはいるための大きなアクセスドアがボルトで止められている。

環境制御システム:Environmental Control System
ECS(環境制御システム)は、IUとS-IVB上部に納められた機器を冷却する。 IUとS-IVB上部には、全部で16個の"cold plate"と呼ばれる冷却板が取り付けられている。 この中には、60%のメタノールと40%の水でできた不凍性の冷却液が、IU内部のリザーバータンクから供給されている。 打ち上げ前は、冷却液の冷却は、地上施設により行われる。打ち上げ約163秒後、IUに搭載された昇華式熱交換機が作動開始する。 誘導コンピュータや飛行制御コンピュータ、ST-124-Mシステムなど、とくに高熱を発生する装置には、より効率的に冷却を行うため、機器内部にも冷却液が循環している。 冷却液と水は、窒素ガスによって循環させられる。

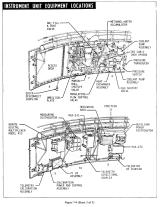
誘導・飛行制御:Guidance and Control
IUの誘導/飛行制御コンピュータは、ロケットの位置、速度、高度、エンジン出力を制御する。 このコンピュータの主要な構成要素は、ST-124-M:慣性プラットフォーム、 LVDC(Launch Vehicle Digital Computer)、LVDA(Launch Vehicle Data Adapter)、 アナログ飛行コンピュータ、ジャイロである。 LVDCは制御の中心となるコンピュータシステムで、各種入出力機器(センサなど)がLVDA経由で接続されている。 これら制御装置は三重化されていて、どれか1つのシステムが他とは異なる計算結果を出力したときは、それは無視される。 さらに、LVDCのメモリは二重化されており、一方のメモリでエラーが検出されると、もう一方の内容で訂正される。

ロケットが大気中を上昇しているときは、誘導システムは、大気の圧力が最も小さくなるように姿勢制御を行う。 また、S-IC、S-IIの切り離しタイミングは、燃料の残量を元にIUが指示する。 S-IIによる飛行中は、 LVDCが、ミッションにもっともふさわしい飛行コースをとるよう制御する。 地球軌道周回中には、地上からの指示で、LVDCの誘導情報を更新することができる。
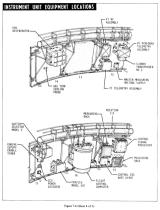
計測機器:Instrumentation
次回のミッションの参考にするため、ロケットの動作、空気圧、騒音レベル、温度、振動、電圧、電流 など数百に上る項目についてセンサで計測され、テレメトリデータとして地上に送信される。 地上、大気圏飛行中、宇宙空間飛行中とミッションの進行にあわせ、計測するデータの種類は選択され、 その時々により重要なデータを送信する。 ステージ切り離し時、レトロ(逆噴射)ロケットが作動すると、その影響でテレメトリデータが乱れる。 このため、ステージ切り離しの間はデータは自動的にテープレコーダに記録され、後で送信される。

追跡システム:Tracking System
RFのパルス信号をSaturnVに向けて発信すると、IUに搭載されたトランスポンダがこれを受信し、 応答のパルス信号を返信する。 これを複数の地上局で受信することにより、ロケットの位置が確定できる。 SaturnVには、AZUSA、Cバンドレーダー、Sバンド コマンド & 通信システム の 3種類の追跡システムが搭載されている。これらを通して、IUに搭載されているコンピュータの メモリダンプや書き換えなども行うことができる。
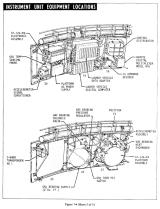
電源:Electrical System
打ち上げ前は、umbilical(へその緒)コネクタ経由で地上から電源が供給される。 そして打ち上げの約25秒前、IUに搭載された4台のDC28Vバッテリに切り替わる。 飛行中は電力消費を押さえるため、LVDCとLVDAが必要のない機器の電源を切る。
コンピューター
Saturn Vのガイダンス&ナビゲーションを含め、アポロ計画で使用されたコンピューターについてのより詳しい情報は、下記のページをご参照ください。関連書籍・ビデオ
-
The Apollo Guidance Computer: Architecture and Operation

Praxis 2010/7/11 5,004円
The technological marvel that facilitated the Apollo missions to the Moon was the on-board computer. In the 1960s most computers filled an entire room, but the spacecraft’s computer was required to be compact and low power. Although people today find it difficult to accept that it was possible to control a spacecraft using such a ‘primitive’ computer, it nevertheless had capabilities that are advanced even by today’s standards. This is the first book to fully describe the Apollo guidance computer’s architecture, instruction format and programs used by the astronauts. As a comprehensive account, it will span the disciplines of computer science, electrical and aerospace engineering. However, it will also be accessible to the ‘space enthusiast’. In short, the intention is for this to be the definitive account of the Apollo guidance computer.
-
Digital Apollo: Human and Machine in Spaceflight

The MIT Press 2011/9/30 2,778円
As Apollo 11's Lunar Module descended toward the moon under automatic control, a program alarm in the guidance computer's software nearly caused a mission abort. Neil Armstrong responded by switching off the automatic mode and taking direct control. He stopped monitoring the computer and began flying the spacecraft, relying on skill to land it and earning praise for a triumph of human over machine. In Digital Apollo, engineer-historian David Mindell takes this famous moment as a starting point for an exploration of the relationship between humans and computers in the Apollo program. In each of the six Apollo landings, the astronaut in command seized control from the computer and landed with his hand on the stick. Mindell recounts the story of astronauts' desire to control their spacecraft in parallel with the history of the Apollo Guidance Computer.
-
Saturn V Apollo Lunar Orbital Rendezvous Planning Guide

Apogee Prime 2011/07/15 USD24.95
The Saturn V Apollo Lunar Orbital Rendezvous Planning Guide is a reprint of a rare document from the early 1960s in which the whole Apollo moon landing mission was presented and illustrated. The book includes a large fold-out of the Apollo mission as well as a fold-out of the Saturn V moon rocket. It includes illustrations of early iterations of the Lunar Module, maps of the Cape Canaveral launch sites, launch schedules for all of the Apollo test flights, detailed specifications and schematics of the Saturn V launch vehicle stages, construction schedules, engine summaries, information on the VAB, mobile crawlers, Umbilical towers, a DVD and more
-
Mission Control

Gravitas Ventures 2017/07/27 USD24.99
At the heart of the Apollo space program and a remarkable decade of achievement was the team who worked in Mission Control.They were born against a backdrop of economic turmoil and global conflict. Some came from a rural lifestyle little changed from the 19th century. Others grew up in a gritty, blue-collar America of mines and smoke stacks. They ranged from kids straight out of college to those toughened by military service. But from such ordinary beginnings, an extraordinary team was born. They were setting out on what JFK called: “The most hazardous, dangerous, and greatest adventure upon which mankind has ever embarked” and through their testimony ? and the supporting voices of Apollo astronauts and modern NASA flight directors ? the film takes us from the faltering start of the program through the Mercury and Gemini missions, the tragedy of the Apollo 1 fire to the glories of the Moon landings.
-
デジタルアポロ ―月を目指せ 人と機械の挑戦―

東京電機大学出版局 2017-01-20 2,700円
洋書Digital Apollo: Human and Machine in Spaceflightの翻訳。 2008年米国航空宇宙学会賞受賞作品。待望の翻訳。国の存亡やパイロットの生死を賭けた壮大なプロジェクト。失敗が許されない極限状態の中、人はどこまで「機械」に任せるのか。意思決定や最終判断は人が担うのか、「機械」が決めるのか。AIやIoTが一般的になりつつある現代において、人と機械、人とコンピュータはどうあるべきか、史実から未来を見つめる。