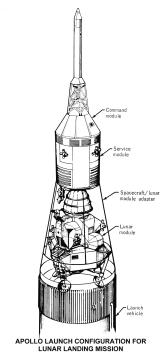
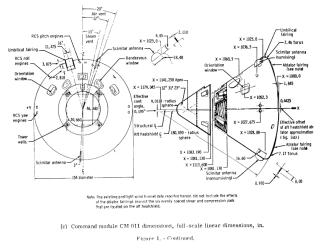
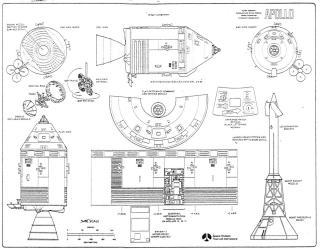
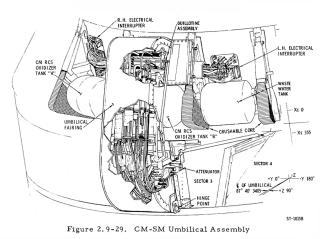
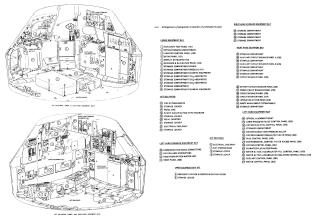
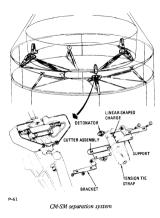
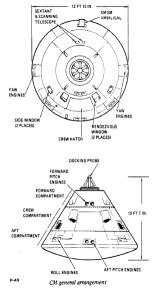
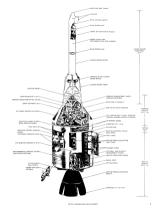
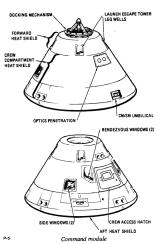
Command Module(CM)
- Height : 10ft 7in (3.2258m)
- Diameter : 12ft 10in (3.9116m)
- Maximum Weight (include crews) : 13000lb (5.902ton)
- Splash down Weight : 11700lb (5.3118ton)
- Fuel load capacity : RCS fuel-monomethylhydrazine; oxidizer-nitrogen tetroxide:270lb(122.58kg)
- Manufacturer : North American Rockwell Corp. Space Div., Downey, Calif.
Structure


Cockpit
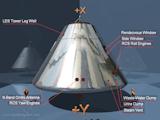
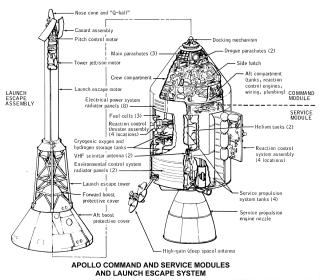
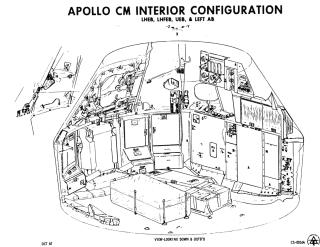
The cockpit is divided into three parts. The docking tunnel is the forward compartment. The crew compartment is the area in which the astronauts spend their time. Finally, there is an aft compartment in the back of the CM.
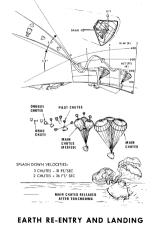
The forward compartment is separated by a bulkhead from the cabin, and is divided into 4 areas at ninety-degree angles. Earth landing equipment like parachutes and beacon lights are stored here. This area is covered with the forward shield cover, which is installed under the LES legs. This cover is jettisoned with when the CM is at approximately 25,000 feet after re-entry, preparing for the deployment of the parachute.

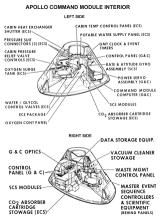
Cabin

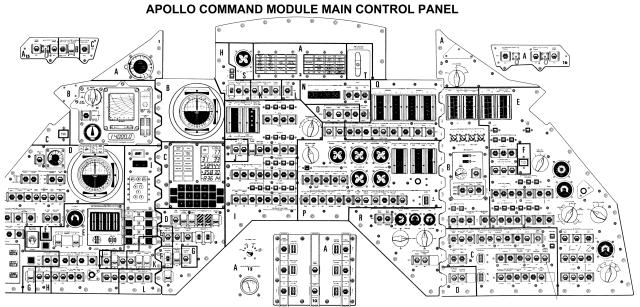
Materials such as water and food are packed and stored in the wall on the side of the cabin. After launch, the astronauts remove their spacesuits, and wear overalls in the cabin. The astronauts normally only wear their spacesuits during launch, LM docking and undocking, moving between CM and LM, EVA, and re-entry. The commander usually handles the operation of the ship, while the CMP does navigation, and the LMP monitors and operates the sub-systems. While the CDR and LMP are on the surface of the moon, the CMP handles observation of the surface and serves as a communications relay between the Earth and LM, in addition to the normal work of the CDR and LMP. Of course, all three astronauts are trained in all systems and procedures, so that in the event of an emergency, even a single person can still safely return to the Earth.

Two nitrogen gas bottles and cylinders are installed into the cabin's hatch. When an emergency occurs during launch, one of the bottles is used for explosively opening the hatch. After a normal launch, the contents of this bottle are vented into space. The other bottle is used for explosively opening the hatch after splashdown. The hatch also has a valve that can vent the cabin atmosphere in one minute.
The cabin has five windows, made of 0.25-inch (6.35mm) double-paned tempered glass on the inside, and 0.7-inch (1.778cm) amorphous-fused silicon on the outside. UV-ray blocking coating is applied in these outer surfaces, and non-reflective coating to the inside. The outer glass can stand up to a maximum temperature of about 1540 degrees Celsius (2800 Fahrenheit). A covering shield made of aluminum is installed inside all of the windows. A mirror to confirm the deployment of the parachutes during re-entry is installed over and under the right rendezvous window.
AFT compartment

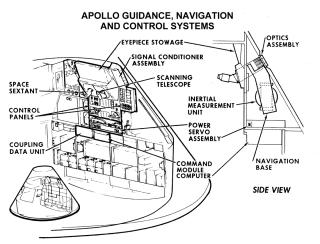
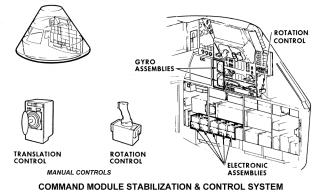
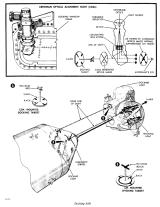
Many important materials are stored in the lower equipment bay, underneath the astronauts' feet, such as the navigation station, guidance and navigation electronic equipment, sextant to determine position in space, the telescope, a computer and keyboard (DSKY), batteries, and the communication system. Food and science observation materials are stored in compartments here.
The main materials of the environmental control subsystem are stored in the left bay. This also is where the hatch is stored after the CSM and LM dock.

The waste management system controls and equipment, electrical power equipment, and other electronics are stored in the right bay. Some of the food is stored here, too.
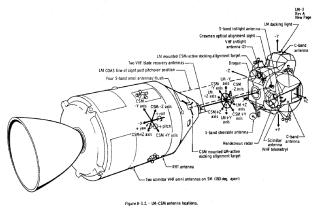
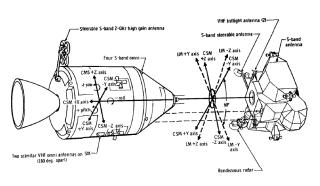
Bays behind the astronauts are where the spacesuits and helmets are stored. Life vests, the fecal canister, portable life support systems (PLSS backpacks), and other equipment are stored here. The probe and drogue assembly used for docking with the LM is stored here as well.
Drawings

And on their Spaceship Panelmaniacs page, you can study about the cockpit detail of Apollo, Mercury, Gemini, even Vostok and Soyuz.
CSM COLOR CHART
| CSM-012 Apollo1 |
|---|
| BLOCK1. RCSs align tandem above hatch. Scimitar antenna on CM. Appearance of SM is very different toward BLOCK2. |
| CSM-017 Apollo4 |
|---|
| BLOCK1. EVA handle and Sea Recovery Tether Ring are added on CM. |
| CM020&SM014 Apollo6 |
|---|
| BLOCK1. Two more EVA handles are added on CM. |
| CSM-101 Apollo7 |
|---|
| BLOCK2. No docking plobe. |
| CSM-103 Apollo8 |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-104 Apollo9 Gumdrop |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-106 Apollo10 Charlie Brown |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-107 Apollo11 Columbia |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-108 Apollo12 Yankee Clipper |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-109 Apollo13 Odyssey |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-110 Apollo14 Kitty Hawk |
|---|
| BLOCK2. |
| CSM-112 Apollo15 Endeavour |
|---|
| BLOCK2. J mission. SIM(Scientific Instrumentation Module) Bay at Sector 1. |
| CSM-113 Apollo16 Casper |
|---|
| BLOCK2. About the same specification with CSM-112. |
| CSM-114 Apollo17 America |
|---|
| BLOCK2. About the same specification with CSM-112. |
Related books and videos
-
Apollo Spacecraft - News Reference

Periscope Film LLC / ApogeeBooks 2005/11/26 USD60.00
The Ultra Rare and Coveted Apollo News Reference Manuals. These books have become legendary amongst the space collecting fraternity and have been known to sell at auction for as much as $6,000 for the pair. Now as a valued customer Apogee is proud to offer these beautiful replicas to add to your collection of Apogee Space Books. Each book comes with an accurate replica of the original 1960's cover and the pages are set out in the same sequence as the originals. Almost 500 pages of in depth detail about the Apollo spacecraft in the exact words of the contractors who built them.
-
Virtual APOLLO

Scott P. Sullivan / Apogee Books 2003/02/18 USD38.37
With this book readers can become acquainted with the Apollo spacecraft in detail and learn the story of its design and construction.